1 Introduction
Work-life balance refers to achieving a balance between professional and personal life through the management, organization and prioritization of personal tasks and work routines ( FAZAL et al., 2019 ). Several researches suggest that academic administration develop strategies for maintaining and developing the work-life balance of teachers in their academic careers (AMITH; VINAY; GOWRAMMA, 2019; SONI; BAKHRU, 2019 ).
Considered as the fundamental asset in Higher Education institutions (HEIs), the teacher plays a representative role in the execution of organizational objectives and their performance influences the learning process and student results ( GOODING, 2018 ; SETHI et al., 2017 ), directly intervening in the goals of any Education program (JOHNSON; WILLIS; EVANS, 2019). Research has identified that teachers presented the most unstable work-life balance when compared to other positions in Higher Education institutions ( BEER et al., 2015 ; KANG; PARK; PARK, 2019). Studies that analyzed the teachers’ work-life balance have limitations in terms of explaining the specific aspects that contribute to this instability (EBERMAN; SINGE; EASON, 2019; KRUEGER et al., 2017 ; NILSSON; BLOMQVIST; ANDERSSON, 2017). The understanding of work-life balance indicators is representative in this research audience, since the well-being of teachers can influence their productive effectiveness in teaching, research and management, ultimately interfering in the quality of Higher Education (ABRAMOV; GRUZDEV; TERENTEV, 2017).
The absence of favoring the work-life balance in the face of teachers who work in the university environment can affect their commitment both in the area of teaching and in research, and can also generate distance from family commitments. The work-life balance of teachers can be an attenuator not only for the quality of Education, but also to make undergraduate and graduate programs more sustainable, with impacts in the short and long time ( BEER et al., 2015 ; DEVI; LALU, 2018 ; ZEHRA; RUKHSANA, 2020 ). Therefore, it is something that demands from teachers, during the career formation period, to receive an adequate structure so that the work environment can remain healthy. Higher Education teachers face continuous tension regarding the quality of classes, publication of scientific research, excessive workload, deadlines, constant performance evaluations by programs, requirements for frequent participation in academic events, among other activities inherent to the profession (BEIGI; SHIRMOHAMMADI; KIM, 2016; DUBAS-JAKOBCZYK et al., 2020 ; JOHNSON; WILLIS; EVANS, 2019).
Insecurity in living with the coordinators is aggravating stress ( BERHEIDE et al., 2020 ; PU et al., 2017 ), as well as the various activities that university teachers carry out, in their personal lives as parents and in career building also as students, and in professional life as researchers and employees ( MCCUTCHEON; MORRISON, 2018 ). Regarding the number of factors that generate aggravating stress and the job responsibilities of teachers, maintaining the balance between professional and family life becomes another challenge ( FAZAL et al., 2019 ). Due to the conflicts generated between professional and family environment, some teachers in career construction give up academic life soon after finishing the doctoral course, exercising other professions ( CABAY et al., 2018 ). However, there are data that show that Higher Education institutions do not favor the career building of teaching professionals. Instead, the work environment at universities is seen as expensive by several teachers, which influences the work-life balance in a harmful way (JAIN; MISHRA; YADAV, 2018).
Research on the work-life balance of Higher Education teachers and other professionals working at universities has deepened in factors such as stress level ( DEVI; LALU, 2018 ), workload ( SALTMARSH; RANDELL-MOON, 2015 ) and production scientific ( YOU, 2016 ) in isolation, instead of using a global approach, as it would allow to consider several related aspects in the development of the work-life balance ( KRUEGER et al., 2017 ; SMELTZER et al., 2016 ). Therefore, after researching the literature, this article aims to analyze the work-life balance and the impact on the well-being of Higher Education teachers, through a systematic review of the existing literature, answering the following questions: (i) What are the main impacts of work-life balance on the well-being of Higher Education teachers? (ii) What are the main strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats for the development of the work-life balance of Higher Education teachers?
The research is structured as follows. This first section presents the introduction and the objectives proposed in the study. The next section presents the methods used to carry out the research. Following are the main results found and, in closing, the conclusion of the study.
2 Methodology
This study has retrieved data from the ScienceDirect, Scopus and Web of Science, a comprehensive database that has been used extensively by various researchers for carrying out systematic reviews ( NORRIS; OPPENHEIM, 2007 ; SEDIGHI, 2016 ). The choice of databases is justified by being the largest bases of bibliographic references and abstracts of the scientific literature of peer review. This provides a multidisciplinary scientific analysis with the integration of innovation, technology and applied research ( ARCHAMBAULT et al., 2009 ). According to Norris and Oppenheim (2007) , ScienceDirect, Scopus and Web of Science feature coverage of high-impact articles and extensive bibliographic coverage in the area of Social Sciences.
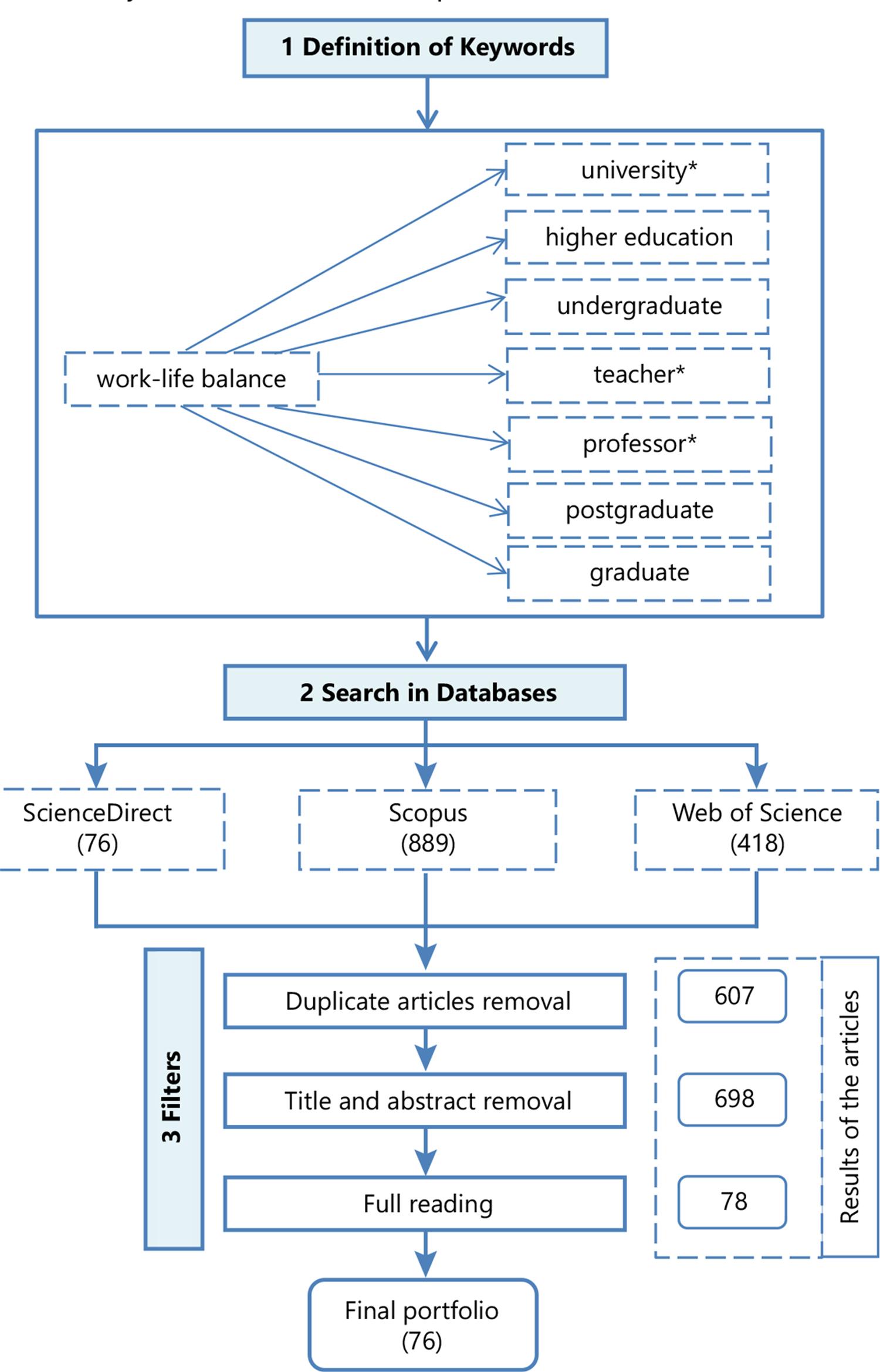
The set of keywords used in the search was defined using Boolean operators and truncation symbols (see Figure 1 ). After searching the databases, 1383 articles were found. The authors did no limit time coverage. Thereafter, to select articles of relevance for the study, filtering procedures were adopted. The following criteria were used: (a) exclusion of duplicates using Mendeley (version 1.17.13) and EndNote X6; (b) restriction for inclusion of articles and review, eliminating books, book chapters and conferences; and (c) articles not related to the proposed theme were deleted – filter by title and summary, followed by full reading.
In total, 607 duplicate articles were eliminated; thus, of the 1,383 remained 776. After the title filter, since there were studies that did not fit in this research, there were 477 left. The filter by abstract was also applied and after reading the abstracts, 246 articles that did not fit the theme were identified and eliminated, and therefore, a total of 723 articles were eliminated by titles and abstracts. At last, after full reading of the articles, 53 articles have been selected for the final portfolio in a rigorous methodology of systematic review.
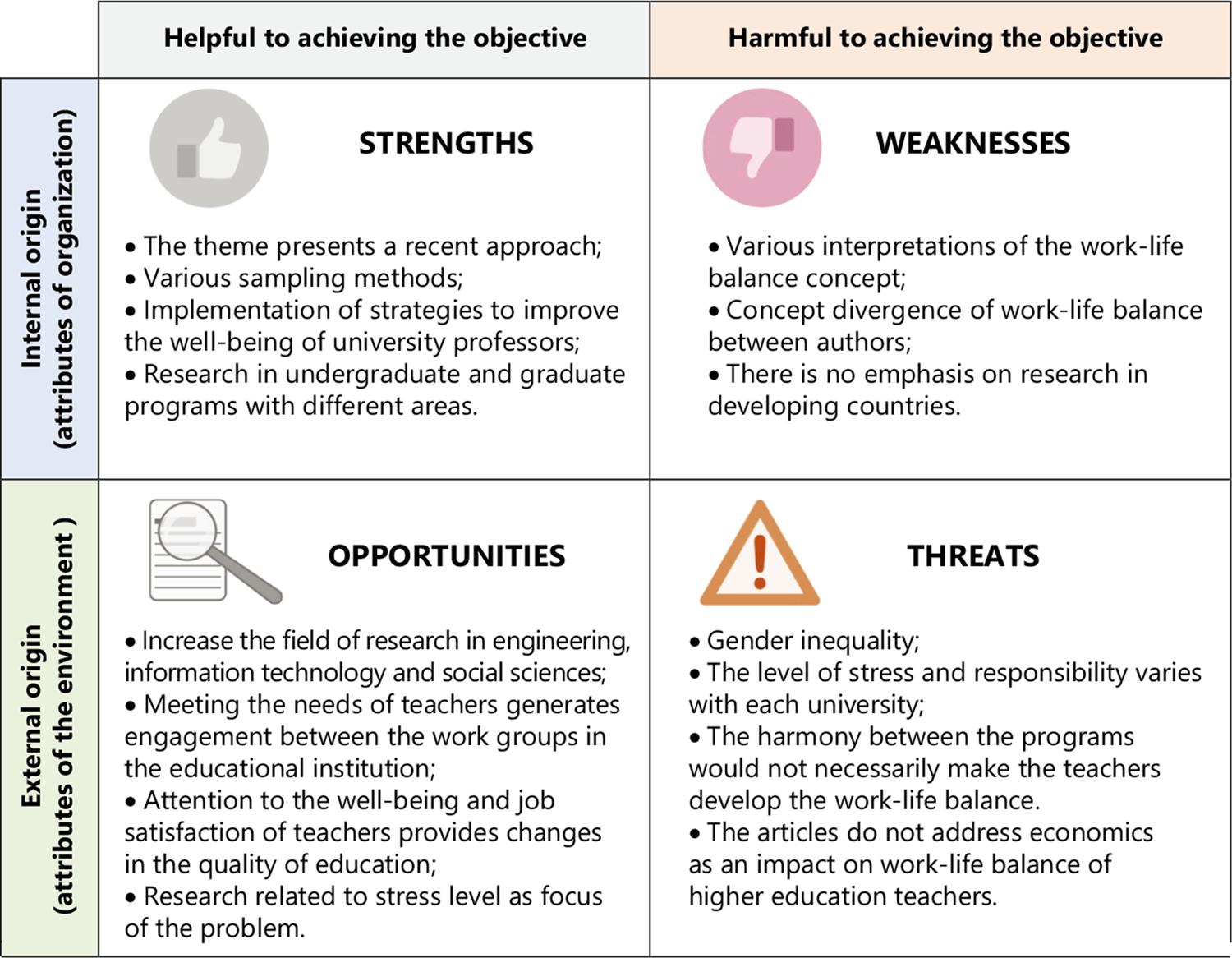
The final portfolio of the 53 articles is analyzed in the results section, in which the articles were organized by bibliometric analysis and the VOSViewer® software was used to construct visual maps ( VAN ECK; WALTMAN, 2009 ). Bibliometric analysis manifests interconnections among the articles in respect of the frequency with which an article is cited and co-cited by other articles (BESSELAA; HEIMERIKS, 2006). The following techniques of bibliometric analysis have been adopted for this study: citation analysis, and co-occurrence of terms/words. The SWOT analysis was carried out to address the proposed research questions of this study (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats – the initials SWOT). The business strategy tool was invented by a group of Harvard teachers: Learned, Christensen, Andrews and Guth - in order to identify strategic options for a business or project ( LEARNED et al., 1965 ). The citation analysis discusses the countries, institutions, journals and articles that have been scientifically influential according to the number of citations ( DZIKOWSKI, 2018 ). In addition, main topics discussed about the work-life balance, research areas, field of activity (Teaching, research and management) are presented in the literature.
The co-occurrence of terms/words identified the main trends in the field that need to be investigated ( SEDIGHI, 2016 ). In the SWOT analysis, strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats were identified. The significance of SWOT analysis is that it provides a good way to examine both positive and negative attributes within a single analysis, determining how best to build solutions for the problem in analysis ( HELMS; NIXON, 2010 ).
3 Results of the characteristics found in the studies
3.1 Citation analysis
This section considers a total of 53 articles written by 152 authors and co-authors published in 39 journals, from 2005 to May 2020, developed by 18 countries in 46 Teaching and research institutions, with a total number of 455 keywords and 2,286 references cited.
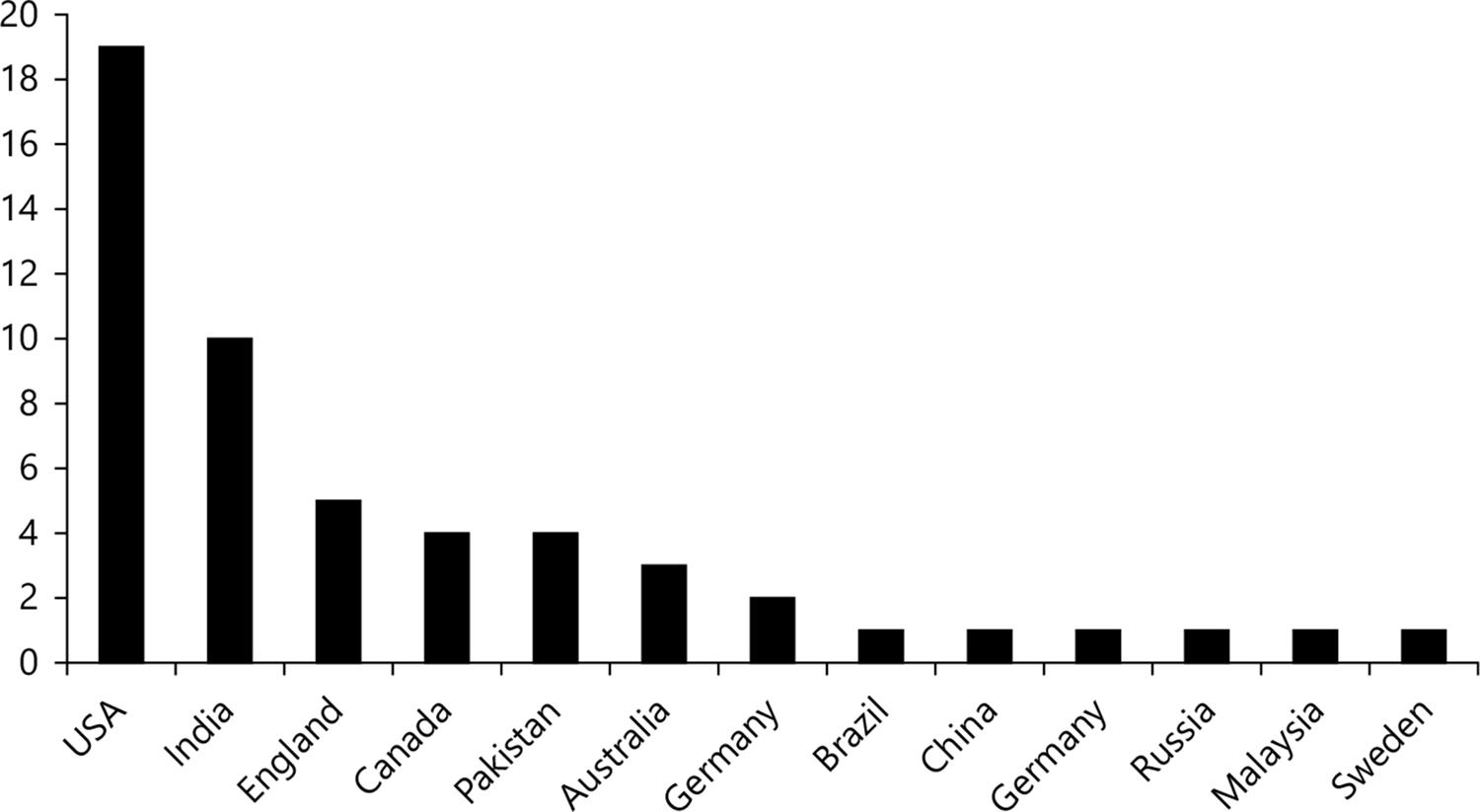
With regard to the number of publications, Figure 2 shows the number of articles per country.
America is the continent with the largest number of publications related to the topic, since 24 of the 53 articles evaluated are from American countries. Asia also appears with a representative contribution of 16 publications. Among the countries with the highest number of searches are the USA (19 articles) and India (10 articles). The continents of Europe and Oceania are those that appear less prominently in relation to the topic addressed, with 10 and 3 articles respectively.
In the United States of America, research was carried out to contribute with new perspectives on the representation of women in HEIs, which revealed some barriers that included gender discrimination, lack of support from the faculty in the workplace, opposition from family members, need to choose between family and professional obligations ( BEDDOES; PAWLEY, 2014 ; FAZAL et al., 2019 ). According to Lester (2015) , Higher Education institutions need to deal with the individual nature of women’s work-life balance considering the scenario of gender inequality. Similarly, India also appears prominently in research on the issue of gender (MARAGATHAM; AMUDHA; MOTHA, 2017; SUMATHI; VELMURUGAN, 2018 ). It was found that career development opportunities are one of the aspects that women most seek to work in the institution. For this reason, women’s retention can be a vital source of competitive advantage in achieving the organization’s goals and objectives, and the scenario is no different in Higher Education institutions ( DHANYA; KINSLIN, 2017 ).
Regarding the institutions, few appear to be involved in more than one study. Only the University of California (3 studies), Faculty of Engineering at Trivandrum (2 studies) and Faculty of Nursing at the University of Villanova (2 studies). The reduced number of articles per institution allows us to infer that there is no study center that focuses on the proposed theme. Regarding the journals, the ones that published the most were International Journal of Stress Management and Journal of Athletic Training, both with 3 studies. It can be seen that the journals that publish the most on the topic work-life balance of Higher Education teachers are focused on the areas of psychology, administration and physical Education. These journals present studies on work-life balance with objectives aimed at the internal aspects of the institution, with an evaluation of the factors that develop a healthy work environment, such as support from co-workers, increased degree of retention of teachers and opportunities for career improvement.
Complementing the analysis, “Appendix A” shows the characteristics of the studies evaluated, presenting the authors, main topics discussed about work-life balance, study areas and practice field (Teaching, research and management). The articles were classified as most influential scientifically according to the number of citations.
Among the 53 articles, three articles with the highest number of citations were: Houston, Meyer and Paewai (2006), who mention that coordinators and teachers should take responsibility for defining their work functions, to build an active role in workload management; Tytherleigh et al. (2005) , who state that the stress of Higher Education teachers is related to job insecurity; and the research carried out by Grawitch, Trares and Kohler (2007), provides initial support to the proposition that teachers’ work-life balance should be integrated into the plans of Higher Education institutions, to ensure that the work-life imbalance does not affect the well-being of teachers and the quality of Teaching.
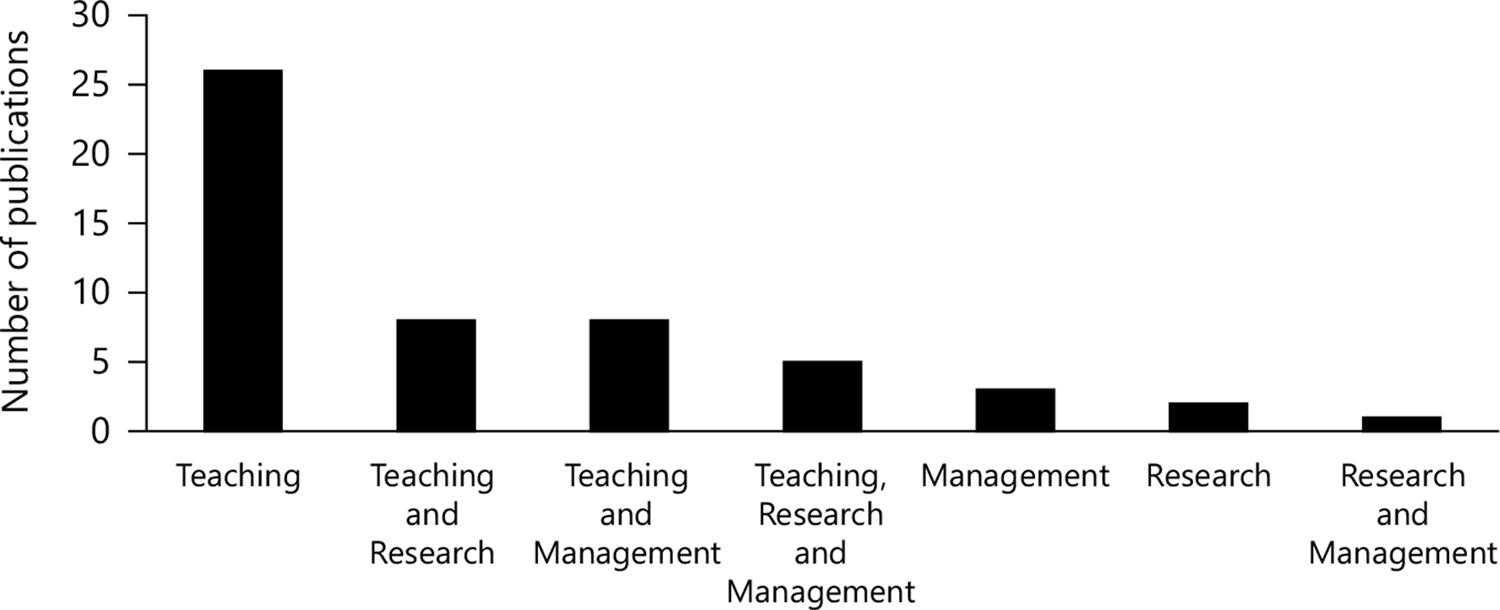
The body of literature demonstrates a diversity of research on the theme of work-life balance of teachers in Higher Education institutions. It appears that most journals belong to areas focused on Education (34.0%), Medicine (30.2%), Administration (28.3%) and Psychology (26.4%), emphasizing that some journals are related in more than one research area. Among the main topics discussed by the authors, gender inequality appears in 24.5% of the studies, followed by the level of stress at work with 22.6% and the absence of a healthy workplace with 15.1%, with some articles classified in more than one topic. Figure 3 shows the list of studies evaluated according to the field of activity.
Most studies, 58.5% focused on the work-life balance of teachers in an isolated work field, with emphasis on Teaching. Among the 53 articles in the final portfolio, 41.5% showed a relationship in more than one field of activity, with Teaching and research as the main emphasis with 17.0% of the studies evaluated. Only 5.7% of the studies within the theme addressed evidenced the Teaching professionals who work specifically in management. This fact is worrying, since professionals who work in the positions of directors and deans are important for decision-making in Higher Education institutions; they are responsible for establishing policies in the workplace to meet the needs of employees to balance professional and personal responsibilities. However, the fact that there is little research that addresses management can be explained by the small number of teachers who work in university management.
3.2 Co-occurrence analysis
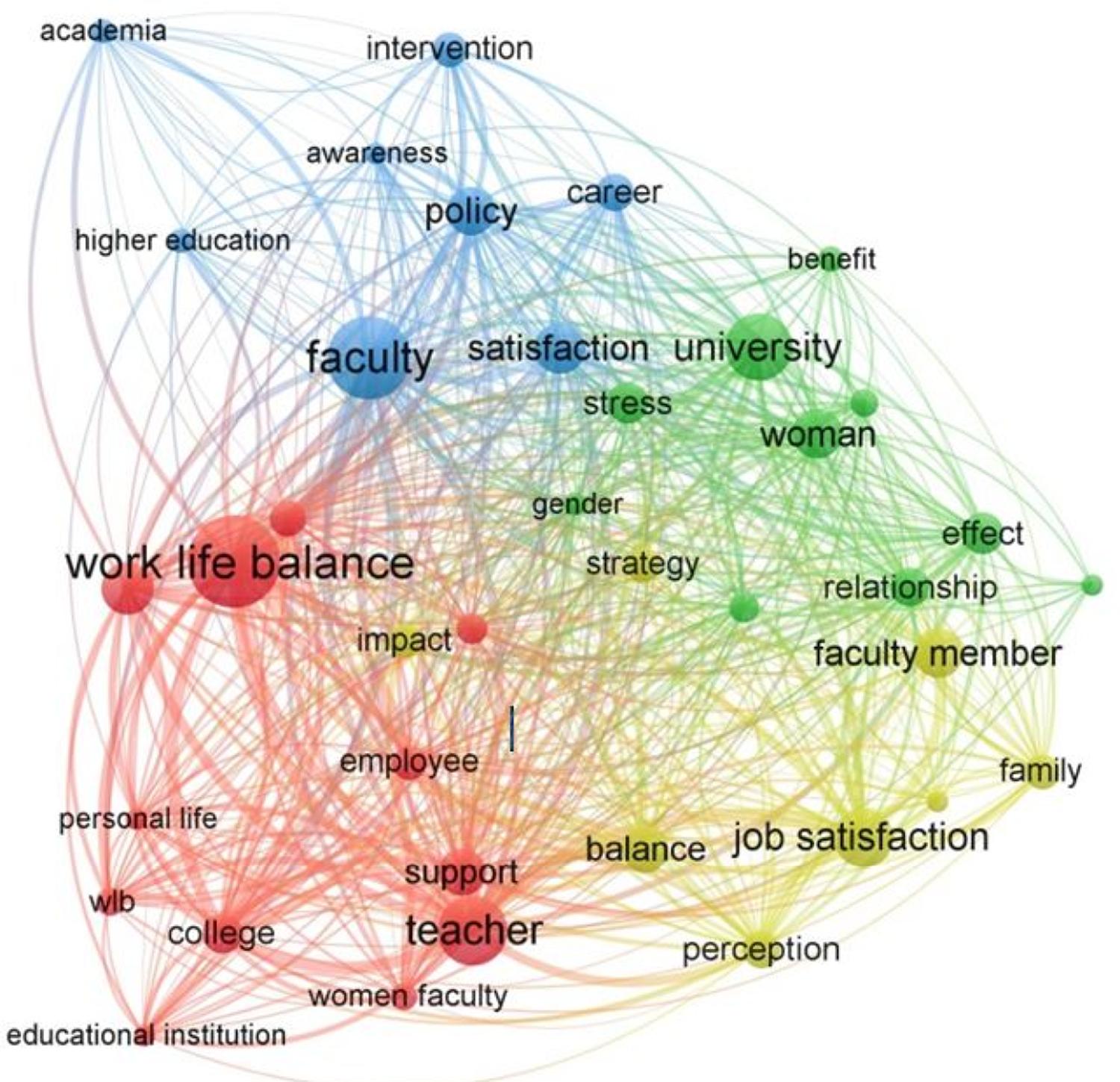
A visual map was created with text data, in which titles and abstracts were considered (see Figure 4 ), the complete counting method was used, with a minimum number of occurrences of 10 keywords, thus 65 terms of a total of 2,291 meet the proposed criterion. Four clusters were identified with 604 elements of link occurrence.
Therefore, from the existing results, it is possible to conclude that terms in red of the largest cluster mainly focus on studies that investigate work-life balance in Higher Education institutions, evaluating forms of support to balance the practices exercised by the members of the faculty in the workplace and in personal life.
The second largest cluster with terms in green demonstrates studies regarding the work-life balance and the effect of the stress of the faculty members, highlighting the teachers’ commitment to the university and how this can generate conflicts between work and family. In addition, the green cluster studies portray the issue of gender to assess whether the personal life of women has a greater impact on Teaching activities when compared to men. The main concerns within the theme addressed, in a general context, produced a result that relates to job satisfaction focused on the context of organizational intervention and productivity improvement.
3.3 Main topics of the SWOT analysis
Based on the concept proposed by Helms and Nixon (2010) , a SWOT analysis was carried out on the final portfolio of articles, identifying the opportunities and threats, as well as the strengths and weaknesses of the proposed theme. Figure 5 presents a SWOT matrix listing the results found in the evaluation of the articles.
Strengths identified were the studies that presented attempts to apply their objectives in practice, proposing strategies to improve work-life balance, such as formulating policies for teachers to improve the organizational climate and reduce gender inequality in undergraduate and graduate programs ( CHUNG et al., 2010 ; DELELLO; MCWHORTER; MARMION, 2018; SALTMARSH; RANDELL-MOON, 2015 ;), organization of seminars on health, well-being and time management (MAKHBUL; SHEIKH; SHEIKH, 2014), in addition to training for coordination with the function of obtaining a structured model to assist institutions to provide feedback in terms of relationship management (EBERMAN; SINGE; EASON, 2019; TOURANGEAU et al., 2015 ).
The different study methods were another strength identified, in which 60.3% of the articles evaluated used questionnaires, 28.2% interviews, 7.7% literature review and, finally, 3.8% interview and document analysis. In addition, the faculty is researched including several programs in the areas of physical Education ( EASON et al., 2018 ; MAZEROLLE; EASON, 2016 ), engineering ( NAYAK; SHARMA, 2018 ; PARAMASIVAM, 2015 ), mathematics ( CABAY et al., 2018 ), nursing ( TOURANGEAU et al., 2015 ), medicine ( KRUEGER et al., 2017 ), pharmacy ( LINDFELT et al., 2018 ), administration ( DHANYA; KINSLIN, 2017 ; SMELTZER et al., 2016 ), among others, at the undergraduate and graduate levels. However, only 14.1% of the studies made comparisons between programs in different areas.
A weakness identified in the literature was the definition of the “work-life balance”, which can generate doubt in the interpretation. The work-life balance is conceptualized in different ways in research and related to other concepts, such as health, psychology, management, engagement in the workplace, creating difficulties to differentiate certain concepts objectively. The concept of work-life balance found widely in research in different areas indicates the complexity of well-being in the professional environment of Higher Education institutions.
In general, some divergences are found in the concepts. Kinman and Jones (2008) portray that work-life balance is a way of balancing roles, in which fulfilling the responsibilities of one domain (work) does not harm the other domain (family). Kang, Park and Park (2019) state that the work-life balance addresses not only the structure of conflicts and family, but involves other concerns such as health, leisure activities, personal development and community commitments. Little research in developing countries was another weakness; the theme was highlighted by the United States of America and India.
As an identified opportunity, a way to expand the study on the work-life balance of Higher Education teachers would be to enlarge the research fields to include more studies in the areas of engineering and information technology, which appear with a smaller number of publications in the reviewed articles. These areas present theories that can assist in the interpretation of complex situations, skills and the development of strategies to avoid conflicts in the professional and personal lives of teachers.
The biggest focus of the HEI is on the development of the teachers’ career, quantifying participation in congresses and seminars or publications ( EASON et al., 2018 ; HADLER, 2010 ). Another opportunity would be to value not only career growth, but also well-being and job satisfaction of teachers, as it can provide changes in the quality of Education. Research shows that if teachers have conflicts between family and professional life during the course of building their careers, and may not even continue to work in the area, everyone involved ends up having losses ( CABAY et al., 2018 ; SETHI et al., 2017 ). Therefore, in relation to this divergence are financial expenses, in which there is no investment in psychological resources for teachers due to the expense of dedication in the various responsibilities ( ZEHRA; RUKHSANA, 2020 ).
For teachers who present a high level of stress, strategies formulated by Higher Education institutions with a focus on psychological and social support were seen as effective for improvements in work-life balance ( DEVI; LALU, 2018 ). The opportunity lies in advancing studies on the subject addressed, evaluating how these strategies can be used by Teaching professionals, eventually aiming at achieving the development of the work-life balance.
Finally, the issue of gender can be an opportunity found. Evaluated studies presented the female gender as a research audience (KANG; PARK; PARK, 2019; SUMATHI; VELMURUGAN, 2018 ). Countries such as the United States of America have a uniform gender distribution of Higher Education teachers, since 49.6% are women. Germany and Japan, on the other hand, show a gender disparity with a percentage of female teachers working in HEIs of 39.3% and 28.4% respectively (OECD, 2017). These data demonstrate that there are disparities between countries; however, women and men may have different reactions to job satisfaction, professional and family responsibilities, stress and conflicts, and therefore, equality of representativeness for both genders is fundamental.
Women showed a lower balance between professional and family life when compared to men (DENSON; SZELÉNYI; BRESONIS, 2018; MCCUTCHEON; MORRISON, 2018 ). In addition, some women sought alternative paths and different careers ( CABAY et al., 2018 ). Another identified threat was the reasons such as workload and excessive activities, which generate stress or cause Teaching professionals in Higher Education institutions to choose to change careers ( HADLER, 2010 ; SUMATHI; VELMURUGAN 2018 ).
There is an urgent need to review the failures in the public administrative policies of universities in relation to working time and family. These policies can be provided by universities (public and private) to offer teachers options to manage the work obligations and family needs. Among these policies, the following stand out: i) programs for the management of teachers’ working time, including leisure habits and family support in personal planning ( SALTMARSH; RANDELL-MOON, 2015 ); ii) smaller classes; iii) faculty meetings using flexible methods, for example, virtual meetings (DELELLO; MCWHORTER; MARMION, 2018); and iv) informal work environment (EBERMAN; SINGE; EASON, 2019).
4 Final considerations
This article presented a systematic review of literature on work-life balance and the impact on the well-being of teachers who work in Higher Education institutions. Based on a systematic review of 53 articles retrieved from ScienceDirect, Scopus and Web of Science for the period of 2005 – May 2020, this article presented a rigorous systematic review methodology. From the final portfolio of the articles, some conclusions were drawn.
The main impacts on teachers’ well-being due to the work-life balance, during the course of their careers in Higher Education institutions were: gender inequality, the level of stress at work and tension, career progress, classroom workload, publication of scientific articles, participation in congresses, compliance with deadlines and performance constants by the programs. The results of the SWOT analysis showed among the strengths the proposal of strategies to improve the work-life balance, such as, for example, formulating policies for teachers, like improving the organizational climate, reducing gender inequality in undergraduate and graduate programs, organizing seminars on health, well-being and time management, and training coordination to formulate a structured model of feedback in terms of relationship management. The various concepts of work-life balance identified in the literature were a weakness, with conceptual divergence between the authors. In addition, the lack of research on the proposed theme in developing countries was another weakness identified. In the opportunity, the increase of the research field in the area of engineering, since this area represented only 9.4% of the analyzed studies. As an identified threat, gender inequality was a topic that appeared as the focus of research in 24.5% of the studies, demonstrating the scenario of a traditional society with a mentality that disapproves of the increase in women’s independence.
Higher Education institutions need to develop a more focused approach to the well-being of teachers, which would increase the chances of teachers maintaining their work-life balance during the development of their academic activities and, in the long run, maintaining quality Teaching. This review showed that Higher Education teachers present certain conflicts to balance family and professional commitments. As future research, it is recommended to study the work-life balance and the performance of teachers in universities, evaluating those who exercise the profession as a priority and those who also work in other professions such as health or business.